06/02/2014 06h00
- Atualizado em
06/02/2014 06h00
Cientistas criam prótese de mão que confere sensação de tato a amputado
Sensibilidade é importante para regular a força exercida pela prótese.
Voluntário diz que 'sentiu a mão' pela primeira vez depois da amputação.
Mariana Lenharo
Do G1, em São Paulo
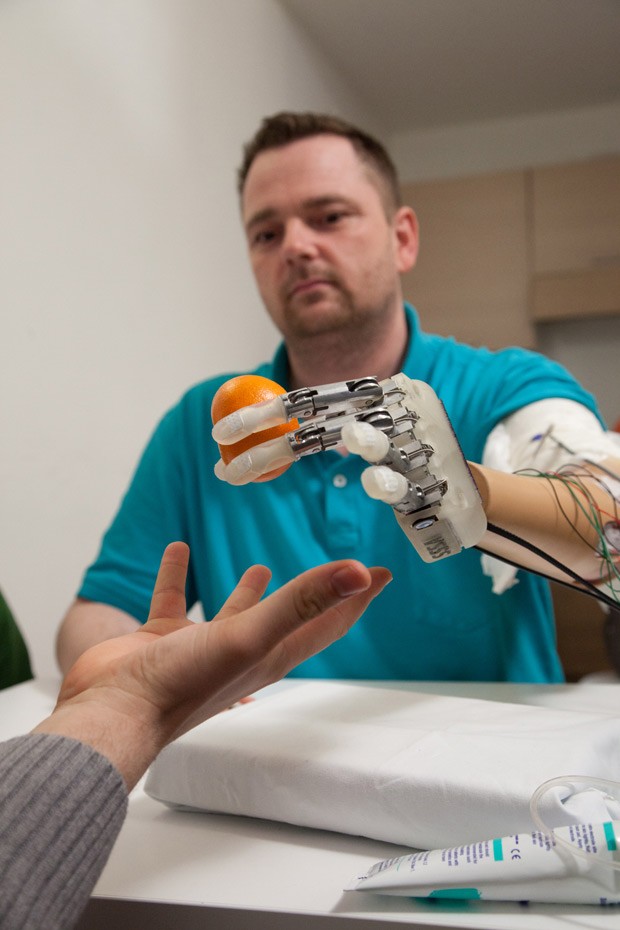
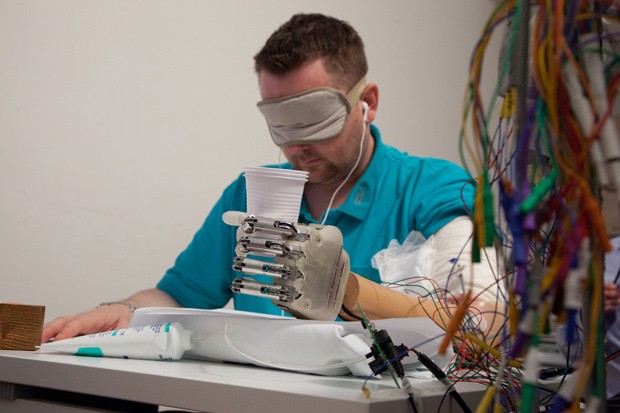 Voluntário
Dennis Aabo Sørensen identifica as características do objeto que segura
por meio de uma sensibilidade artificial (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia
Tocci)
Voluntário
Dennis Aabo Sørensen identifica as características do objeto que segura
por meio de uma sensibilidade artificial (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia
Tocci)
Uma nova prótese de mão desenvolvida por um grupo de pesquisadores
europeus foi capaz de conferir ao amputado uma sensação semelhante ao
tato, permitindo que ele identificasse a forma e a consistência de
objetos. A novidade foi considerada de grande importância, pois a
sensibilidade ao toque é essencial para o controle dos movimentos e da
força.
Podemos não perceber, mas a modulação da força que exercemos ao segurar
um objeto depende das informações que inúmeros sensores presentes em
nossas mãos enviam para o cérebro, informando se o objeto é macio,
rígido, áspero ou pontudo. Sem ter essa sensibilidade, arriscaríamos
empregar força demais, e amassar um copo de plástico, por exemplo, ou
força de menos, e deixar um copo de vidro se espatifar no chão.
O equipamento, criado a partir de uma colaboração entre cientistas de
instituições da Itália, Suíça, Alemanha, Inglaterra e Dinamarca, envia
informações captadas por sensores instalados nas pontas dos dedos da
prótese diretamente para os nervos periféricos do paciente.
“Pela primeira vez, conseguimos restabelecer a capacidade sensorial em
tempo real em um amputado, enquanto ele controlava essa mão
‘sensorizada’”, diz o pesquisador Silvestro Micera, um dos líderes da
pesquisa. O estudo foi publicado na revista "Science Translational
Medicine".
 Voluntário faz bateria de testes para testar tato
Voluntário faz bateria de testes para testar tato
artificial (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci)
Experimento
Os cientistas partiram de um modelo de prótese já existente no mercado,
em que o paciente é capaz de controlar os movimentos da mão artificial
por meio de estímulos elétricos emitidos a partir do esforço exercido
pelos músculos remanescentes. Captados pela prótese, esses estímulos
controlam os movimentos de abrir e fechar os dedos ou girar o punho.
Foram implantados eletrodos diretamente em dois nervos do paciente.
Sensores instalados na mão artificial detectam o nível de força que ele
exerce enquanto segura um objeto. Essa informação é decodificada por um
software e enviada aos eletrodos em forma de sinais elétricos passíveis
de serem interpretados pelos nervos. Dessa forma, o paciente é capaz de
controlar sua força em tempo real para se adequar às características do
objeto.
Para o médico Álvaro Baik Cho, do Grupo de Mão e Cirurgia Reconstrutiva
do Instituto de Ortopedia e Traumatologia do Hospital das Clínicas da
Faculdade de Medicina da USP, o grande avanço dessa técnica é conseguir
fazer uma interface direta da prótese com os nervos do paciente. “Dessa
forma, cria-se uma sensibilidade artificial. É o que eu já vi de mais
próximo a uma sensibilidade normal para o amputado, é realmente uma
coisa muito inovadora”, diz.
O método foi testado em um único paciente: o dinamarquês Dennis Aabo
Sørensen, que perdeu a mão esquerda há 9 anos em um acidente envolvendo
fogos de artifício. Durante a realização de mais de 700 testes, ele
mostrou-se capaz de sentir o formato dos objetos e sua consistência. “O
feedback era totalmente novo para mim e, de repente, enquanto estava
fazendo os movimentos, eu podia sentir o que eu estava fazendo, em vez
de simplesmente olhar o que estava fazendo”, diz o paciente.
Para Cho, ainda deve demorar alguns anos até que essa nova ferramenta
esteja disponível no mercado. Primeiro, o experimento deve ser repetido
em um grupo maior de pacientes. Depois, deve haver um avanço tecnológico
que permita que a ferramenta se torne portátil. O aparelho que
decodifica os sinais captados pelos sensores ainda é grande e pesado.
Toque rudimentar
Uma tecnologia desenvolvida anteriormente já é capaz de fornecer ao
amputado alguns sinais semelhantes ao tato, mas de maneira mais
rudimentar. Trata-se da reinervação muscular orientada (TMR, na sigla em
inglês). Cho explica que, por meio do reimplante dos nervos do membro
amputado sobre os músculos do peito, é possível sentir uma resposta da
pressão exercida pela prótese no peito. Porém, essa técnica não permite
que o paciente tenha uma resposta de modulação da força em tempo real ao
estímulo.
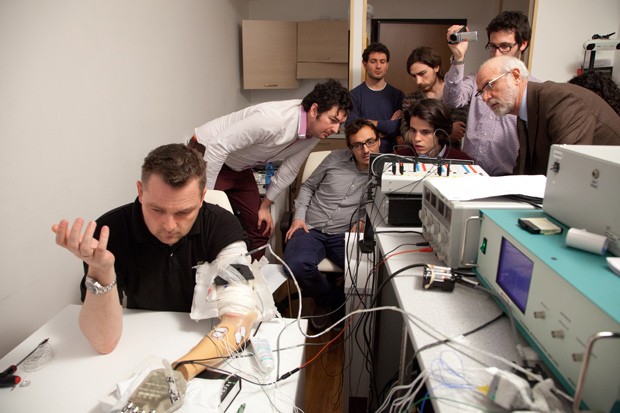 Sørensen é observado por equipe durante os testes da nova prótese (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci)
Sørensen é observado por equipe durante os testes da nova prótese (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci)
02.06.2014 6:00 a.m. - 6:00 a.m. Updated on 02/06/2014Scientists create prosthetic hand that gives the sense of touch to amputeeSensitivity is important to regulate the force exerted by the prosthesis.Volunteer says he ' felt the hand ' for the first time after amputation .Mariana Lenharo The G1 , in São PauloVolunteer Dennis Sørensen Aabo identifies the characteristics of the
object secured by means of an artificial sensitivity ( Photo: LifeHand
2/Patrizia Tocci )A
new prosthetic hand developed by a group of European researchers has
been able to give the amputee a similar feeling to the touch , allowing
him to identify the shape and consistency of objects . The novelty was considered of great importance, because the touch
sensitivity is essential to control the movement and strength .learn more
Projects create prostheses to be fitted with 3D printers
Young gets prosthetic hand that can be programmed for iPhone
Carpenter uses 3D printing to make prosthetics to amputees
Chinese farmer builds homemade dentures replace handsWe
may not realize it, but the modulation of the force exerted when
holding an object depends on the information that numerous sensors send
gifts in our hands to the brain , indicating whether the object is soft ,
hard , rough or pointed . Without this sensitivity , we would venture to employ excessive force ,
and kneading a plastic cup , for example, or less force , and leave a
glass shatter on the floor.The machine , created from a collaboration between scientists from
Italy , Switzerland , Germany , England and Denmark institutions ,
submit information captured by sensors installed in the finger tips of
the prosthesis directly to the peripheral nerves of the patient."
For the first time , we managed to restore sensory capacity in real
time on an amputee , while he controlled this ' sensorizada ' hand,"
says researcher Silvestro Micera , one of the leaders of the research. The study was published in the journal " Science Translational Medicine ."...
Volunteer makes battery of tests to test touchartificial ( Photo: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci )experimentScientists
have estimated a model of the prosthesis already on the market , in
which the patient is able to control the movements of the artificial
hand by electrical stimuli emitted from the effort exerted by the
remaining muscles . Captured by the prosthesis , these stimuli control the opening and closing movements of the fingers or rotate the wrist.Electrodes were implanted directly in two nerves of the patient. Sensors installed in the artificial hand detect the level of force he exerts while holding an object . This
information is decoded by software and sent to the shaped electrodes
that can be interpreted by nerves electrical signals . Thus , the patient is able to control its strength in real time to suit the characteristics of the object .For
medical Alvaro Baik Cho , Group Hand and Reconstructive Surgery ,
Institute of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital das Clinicas,
Faculty of Medicine, USP , the breakthrough of this technique is to make
a direct interface between the device and the nerves of the patient. " Thus , it creates an artificial sensitivity . It's what I 've seen of the closest to a normal sensitivity to the amputee , is actually a very innovative thing , " he says.The
method was tested on a single patient : the Danish Aabo Dennis Sørensen
, who lost her left hand 9 years ago in an accident involving
fireworks. While conducting over 700 tests, it proved able to feel the shape of objects and their consistency. " The feedback was totally new to me , and suddenly , while I was
going through the motions , I could feel what I was doing , instead of
just looking at what I was doing ," says the patient .For Cho , should still take a few years until this new tool available on the market . First , the experiment should be repeated on a larger patient group . Then there must be a technological breakthrough that allows the tool to become portable . The device that decodes the signals received by the sensors is still big and heavy.rudimentary touchA
technology developed earlier is now able to provide the amputee some
similar signs to the touch , but the most rudimentary way . It is oriented muscle reinnervation ( TMR , its acronym in English ) . Cho
explains that through the replantation of amputated nerves on the chest
muscles member , you can feel a response to the pressure exerted by the
prosthesis chest . However, this technique does not allow the patient to have a response of the power modulation to the stimulus in real time.
Sørensen is observed by staff during testing of the new prosthesis (Photo: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci
fisioterapeuta em natal CREFITO-1/7221-LFT
alexandre.fisio1973@gmail.com


 Voluntário
Dennis Aabo Sørensen identifica as características do objeto que segura
por meio de uma sensibilidade artificial (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia
Tocci)
Voluntário
Dennis Aabo Sørensen identifica as características do objeto que segura
por meio de uma sensibilidade artificial (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia
Tocci) Voluntário faz bateria de testes para testar tato
Voluntário faz bateria de testes para testar tato Sørensen é observado por equipe durante os testes da nova prótese (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci)
Sørensen é observado por equipe durante os testes da nova prótese (Foto: LifeHand 2/Patrizia Tocci)